Metatarsalgia: Everything You Need to Know to Manage It
Metatarsalgia: Everything You Need to Know to Deal With It
Metatarsalgia is a painful condition affecting the forefoot, often interfering with walking and making daily activities more difficult. Though frequently underestimated, it deserves close attention in order to prevent complications and improve the quality of life of those affected.
Understanding the Condition
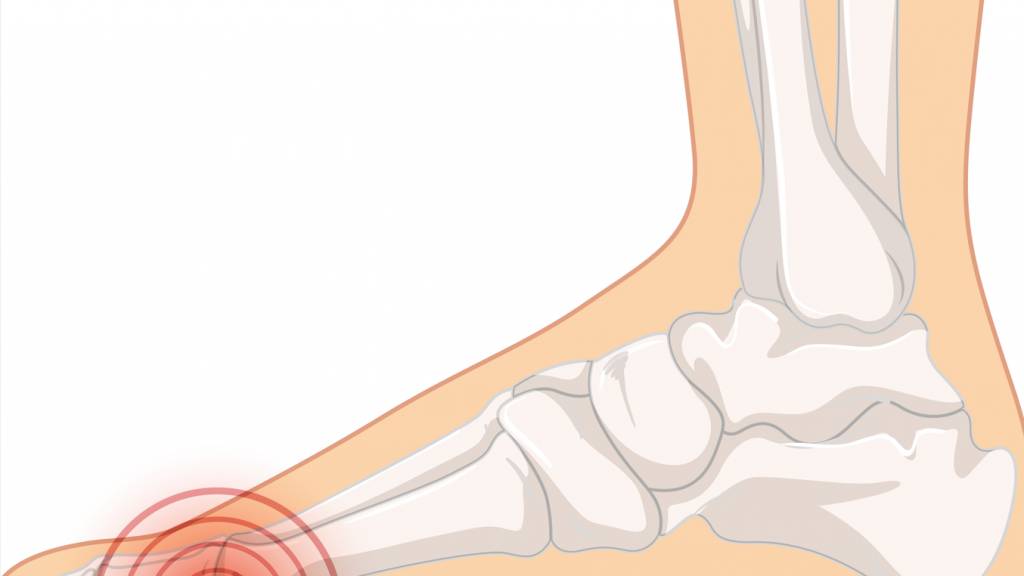
Pain associated with metatarsalgia is typically concentrated in the plantar area beneath the second, third and fourth metatarsal heads. This part of the foot bears continuous loads while walking. An imbalance in weight distribution often leads to inflammation and discomfort. In many cases, altered foot biomechanics are the underlying cause of the condition.
Causes: A Multifactorial Problem
Metatarsalgia may stem from a variety of factors, often in combination. The most common causes include:
-
Structural abnormalities: High arches, flat feet and hallux valgus (bunions) can all alter foot mechanics and increase pressure on the metatarsals
-
High-impact activity: Sports like running and jumping cause repeated microtrauma
-
Inappropriate footwear: High heels and narrow-toed shoes put excessive pressure on the forefoot
-
Systemic diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes may contribute to its onset
-
Obesity: Excess body weight intensifies strain on the foot structures
Symptoms and Daily Life Impact
Pain from metatarsalgia is not merely physical – it can deeply affect a person’s daily life. Even simple tasks become a challenge. The discomfort may manifest as a burning sensation under the forefoot or as sharp pain that limits walking or standing for prolonged periods.
Everyday actions such as climbing stairs, walking or even standing still may become difficult. Pain often intensifies with activities that increase forefoot pressure, such as walking on hard surfaces or wearing unsuitable shoes. This reduced mobility affects independence, mood and overall quality of life.
Common Associated Symptoms
In addition to pain, metatarsalgia can cause:
-
Numbness and tingling: Compression of nerve structures may cause “pins and needles” or a sensation of numbness in the toes
-
Calluses and skin thickening: The body reacts to excessive pressure on the metatarsal heads by forming calluses, which may become painful if left untreated
-
Bursitis: Inflammation of bursae, the small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between tendons and bones, can worsen symptoms and make walking even harder
Compensatory Pain
In some cases, pain is not limited to the forefoot. When pressure is shifted to other parts of the foot or to joints such as the ankle or knee, compensatory pain may occur due to biomechanical changes.
How Metatarsalgia is Diagnosed
Accurate diagnosis is essential for selecting the most effective treatment strategy. The orthopaedic specialist will evaluate:
-
Medical history: To identify habits, trauma or systemic conditions
-
Physical examination: To analyse foot structure and weight distribution
-
Imaging tests: X-rays to assess bone structure, ultrasound for soft tissues and pressure mapping (baropodometry) to study plantar load patterns
Treatment Strategies: From Conservative Care to Surgery
Conservative Treatment
-
Rest and ice: Helpful in the acute phase to reduce pain and swelling
-
Custom orthotics: Insoles designed to correct weight distribution and relieve pressure under the metatarsal heads
-
Physical therapy: Modalities like ultrasound, laser therapy and TECAR therapy can reduce inflammation
-
Anti-inflammatory medications: Always under medical supervision, NSAIDs can help control pain
Surgical Treatment
When conservative methods are not effective, surgical intervention may be needed. Procedures include:
-
Metatarsal osteotomy: Adjusting the length or angle of the metatarsal bones to redistribute load
-
Bunion correction: Addressing hallux valgus to restore better foot mechanics
Prevention: The First Step Toward Well-Being
Preventive habits are essential to avoid the development or recurrence of metatarsalgia. Some practical recommendations include:
-
Wearing shoes with good support and proper fit
-
Using orthotic insoles as soon as symptoms begin
-
Practising foot-strengthening exercises to improve stability
-
Maintaining a healthy body weight to reduce joint strain
Final Thoughts: A Path Toward Recovery
Metatarsalgia can be a debilitating condition, but with a precise diagnosis and a personalised treatment approach, its symptoms can be relieved and active living restored. Working with an orthopaedic specialist, supported by targeted treatments and preventive strategies, is the best way to manage this condition.
If you’re experiencing early signs of discomfort, visit us at our orthopaedics clinic in Via Taramelli 21/23, Bergamo or get in touch today!
? We’re available Monday through Saturday from 9 am to 12.30 pm and from 3 pm to 7 pm at 035 212110
? Or reach us by email at: info@ortopediazambelli.it